5 Tips For Keeping Aged Horses Fit To Compete
Most of the major Western performance horse events focus on horses aged seven and younger, but many horses that once had big limited-age careers can keep showing well into their late teens and early 20s. They might not have the range of motion and athletic ability they did in their younger days — something many human sports legends will attest to — but as long as they are kept fit and in good care, these older horses can still be competitive in weekend, ancillary and horse show classes, or even become teachers for rookies and youth that are getting started in the sport.
Riding and competing with older horses does take some extra finesse, and much like their younger counterparts, those that are kept in a consistent program will find the most success, said Dr. Don Lee, DVM, of Double X Veterinary Services in Sunset, Texas. Quarter Horse News spoke with him to learn more about keeping aged horses fit for competition.
“Aged” Will Vary Between HorsesIt’s hard to pinpoint a number for when a horse is considered aged, as there are several factors, in addition to numerical age, that can cause a horse to slow down. Some horses can develop juvenile arthritis at the age of 3 or 4, for instance, and there are plenty of other soundness issues that might cause a horse to retire early from the limited-age show pen. A good rule of thumb, though, is that once a horse reaches the 15- to 20-year age bracket, you should start watching for signs that he needs to take a few steps back and ease off on hard competition.
“In barrel horses, you might see horses not clock as fast as they used to — they might lose a couple tenths, for instance,” Lee said. “In the cutting world, it’s a little harder as many of them are sore by the time they’re 10 to 12 and have a lot of maintenance. The biggest indicator is losing a step here or there.”
Aged horses might lose their topline and muscle mass as they get older, even if they are used frequently. If you see these symptoms in your horses, they could be indicators that your horse needs some extra care, such as having a veterinarian check him over for arthritis or altering your feeding program to be more senior-friendly.
Diet Can Make or Break Your Aged HorseIn their younger years, some horses might be easy keepers that seem to get fat on air. As horses age, though, especially if they’re getting worked often, their nutritional needs can increase. A horse that might have done well on a forage-only diet could begin to need grain supplementation.
“I like hay better than I like feed a lot of times, but for the aged horses, you often have to supplement some grain,” Lee said. “There’s many good feeds out there, and they’re all fairly comparable, but I recommend a high fat feed and good quality hay.”
Be sure to maintain your horse’s dental care, since it won’t matter how good the quality of the hay or feed you give them is if they’re unable to chew properly. Teeth should be checked regularly, especially in aged horses, as their mouths can change quickly.
“Teeth can be a big part of not only how they ride, but also how they’re able to masticate that feed and absorb the nutrients from the hay and feed you’re giving,” Lee said.
 Regular movement including turnout or exercise can make all of the difference for an aging athlete. * QHN File Photo
Movement Is Essential
Regular movement including turnout or exercise can make all of the difference for an aging athlete. * QHN File Photo
Movement Is Essential
Should your horse’s housing situation require you to leave him stalled all day, keep in mind that a horse that stands around without exercise will be more prone to injury than one that is worked regularly. Therefore, Lee recommended regular turnout for older horses when possible, along with three or four days a week of 30 to 45 minute rides. If turnout is not available, he advised daily exercise, particularly long-trotting.
“A lot of ligament and tendon injuries are injuries of fatigue, so either they don’t do anything with them for two months, pull them out of the pasture, enter them and use them, and then they break down because they’re fatigued and tired, or they’re overworked, and then they break down,” Lee said. “That’s why I like that 30 to 45-minute exercise range. That’s a combination of walk, trot, lope them a little bit, maybe slow work them, things like that.”
Warm-ups and cool-downs are also important, he said. It’s better to give them five minutes of walking before exercise to loosen everything up, and then five minutes to cool down afterward, rather than pulling the saddle off and throwing them back into their stall after a hard ride.
Stiffness Differs From PainIf your horse regularly seems stiff coming out of his stall but eventually works out of it, he likely isn’t in pain, Lee said. Think about older humans when they first wake up in the morning — it often takes a few steps to work out the kinks. Likewise, it can take an older horse’s body a few minutes to loosen up after standing still for several hours.
“It’s just like us — if I sit down for a good period of time and then get up, it takes me three or four strides to get going,” Lee said. “There are different things, like mechanical things, that can create the appearance of lameness, so you have to judge that based on how they respond to flexes. Just because they’re a little stiff doesn’t necessarily mean they’re in pain.”
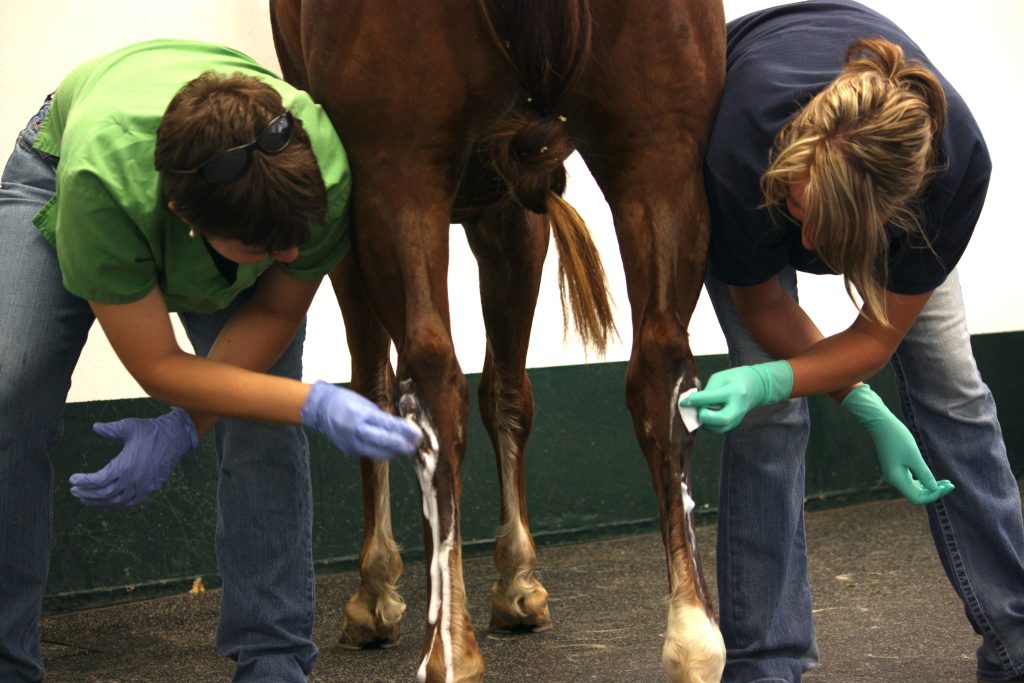 A horse’s hocks get disinfected before injections. * QHN File Photo
A horse’s hocks get disinfected before injections. * QHN File Photo
Horses that have old ligament or tendon injuries in their lower legs can lose range of motion in their ankles and feet. Those horses are still sound, Lee said; they just don’t have as much elasticity as they used to because the tissue may be scarred in from the injury.
No matter how well you care for your horse or keep him legged up, at some point, his age will likely catch up with him. If he still enjoys being ridden and is in good health otherwise, there are supplements, injections and other medical solutions that can help prevent soreness and keep him going under saddle. Talk to your veterinarian about the different options available to see which is the best fit.
Your veterinarian will also be a great source for evaluating your horse’s diet and physical capabilities, and for helping you stay on top of any other care and maintenance needs. These are all crucial for keeping you hauling down the road together.
“I think to keep an aged horse going, regular exercise, a good diet and taking care of their teeth are important,” Lee said. “You never can forget the deworming program, either. That all plays into it as well. But if you’ve got good feed, good feet and good exercise, you can keep a horse going for a long time.”
Mashups and APIs
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.